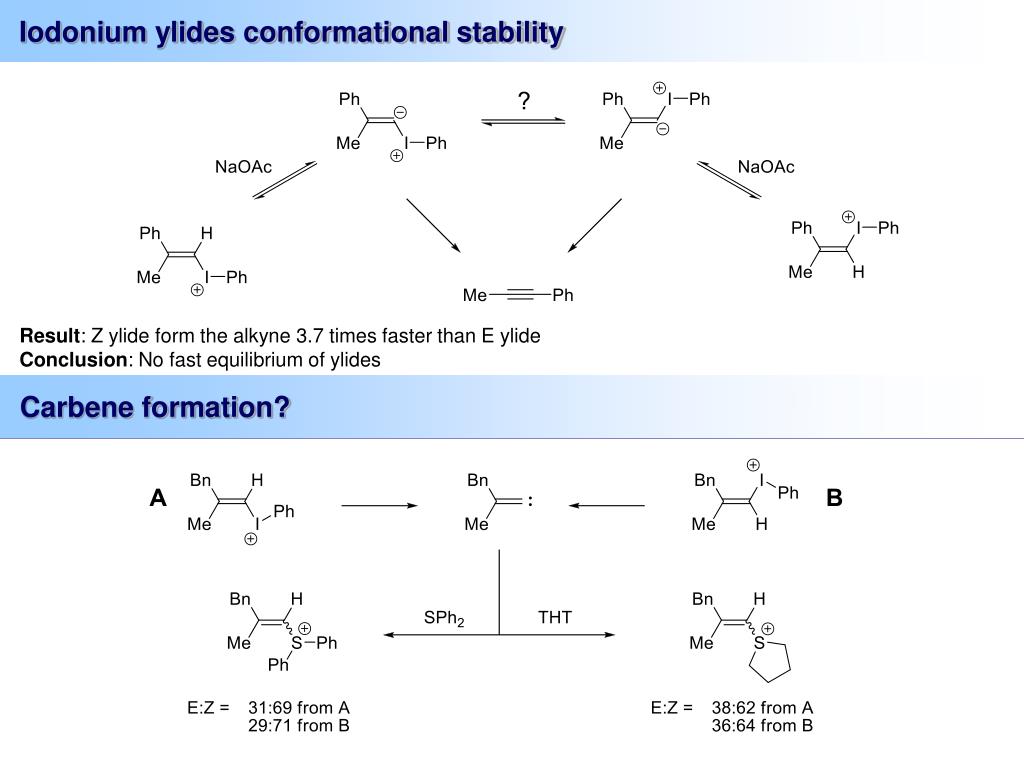
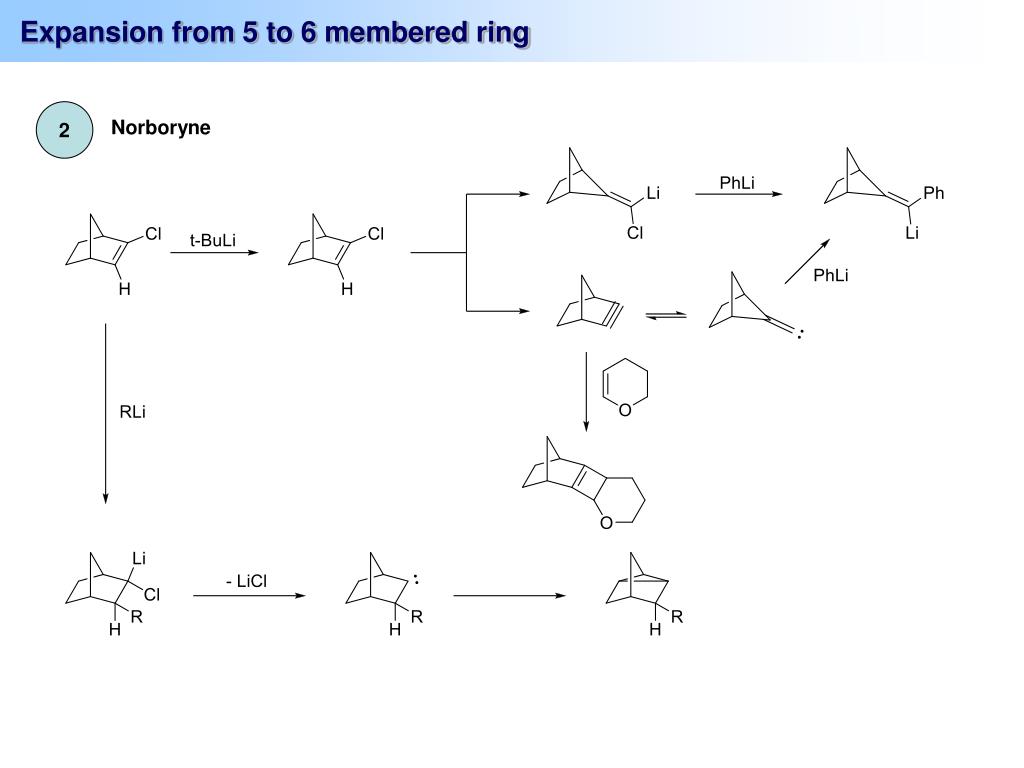
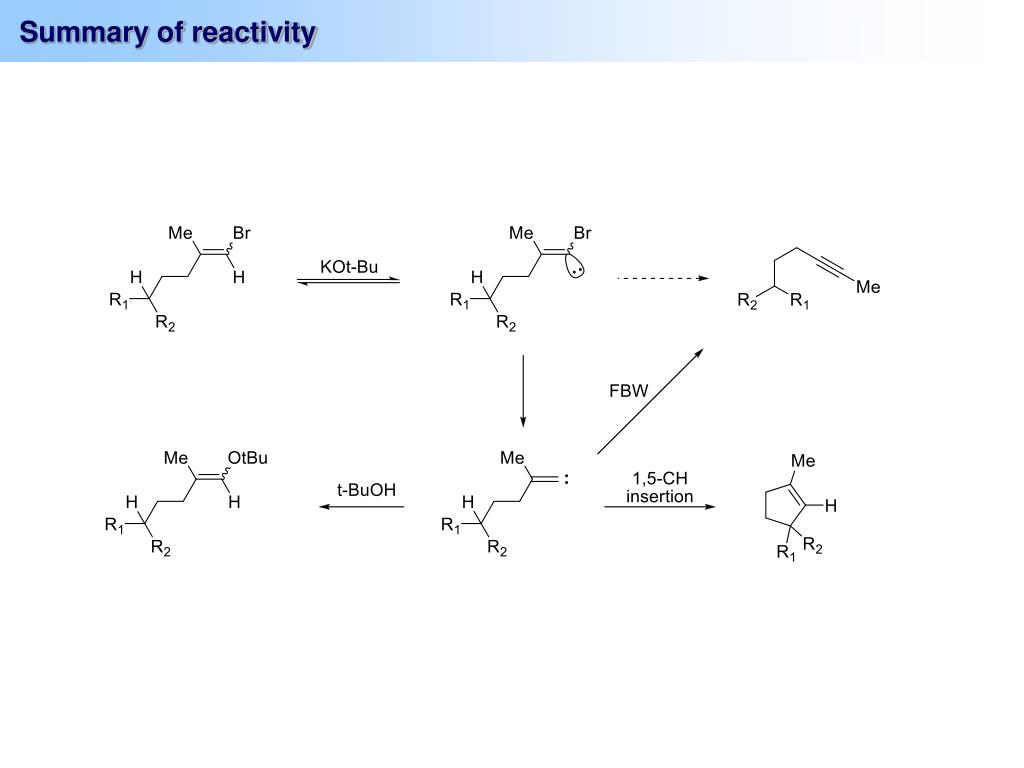
The Fritsch–Buttenberg–Wiechell rearrangement, named for Paul Ernst Moritz Fritsch (1859–1913), Wilhelm Paul Buttenberg, and Heinrich G. Wiechell, is a chemical reaction whereby a 1,1-diaryl-2-bromo-alkene rearranges to a 1,2-diaryl-alkyne by reaction with a strong base such as an alkoxide.
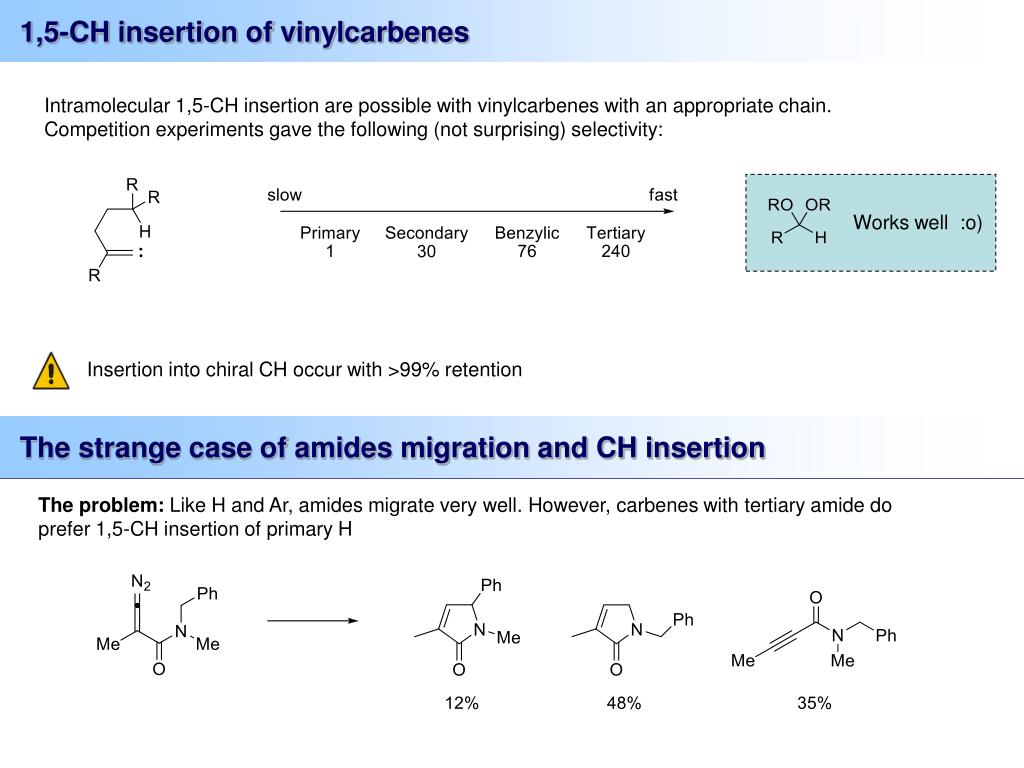
This rearrangement is also possible with alkyl substituents.
Reaction mechanism
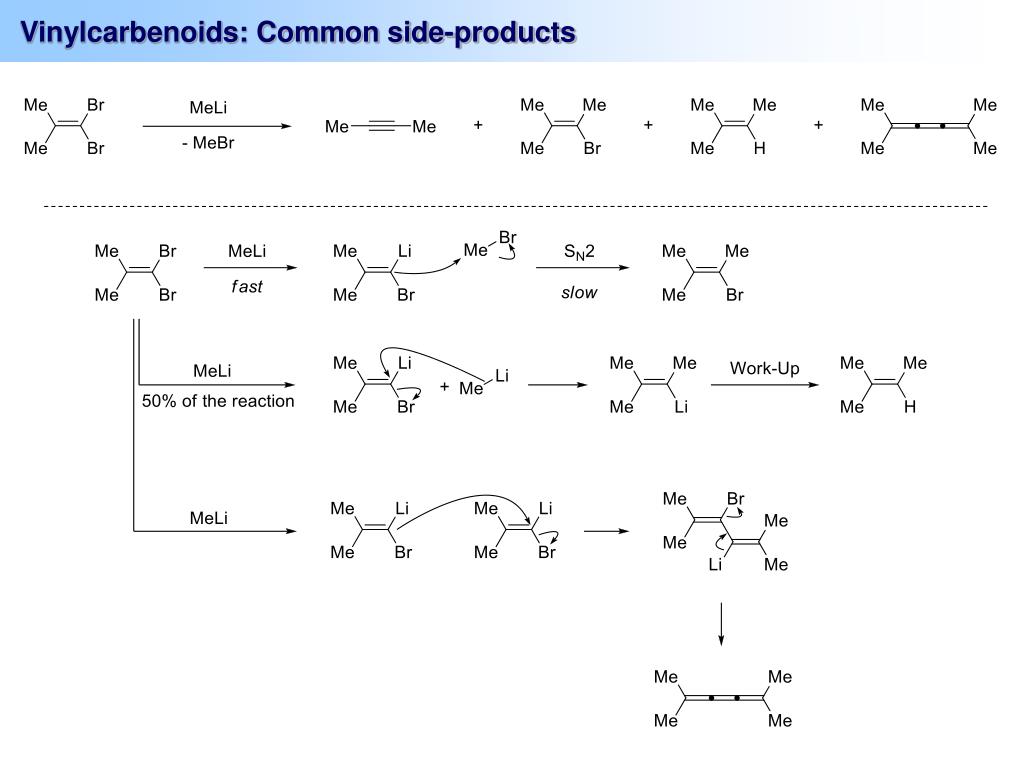
The strong base deprotonates the vinylic hydrogen, which after alpha elimination forms a vinyl carbene. A 1,2-aryl migration forms the 1,2-diaryl-alkyne product. The mechanism of the FBW rearrangement was a subject of on-surface studies where the vinyl radical was visualised with sub-atomic resolution.
Scope
One study explored this reaction for the synthesis of novel polyynes:
See also
- Corey–Fuchs reaction
References
- Darses, B.; Milet, A.; Philouze, C.; Greene, A. E.; Poisson, J.-F. o., Ynol Ethers from Dichloroenol Ethers: Mechanistic Elucidation Through 35Cl Labeling. Organic Letters 2008, 10 (20), 4445-4447.