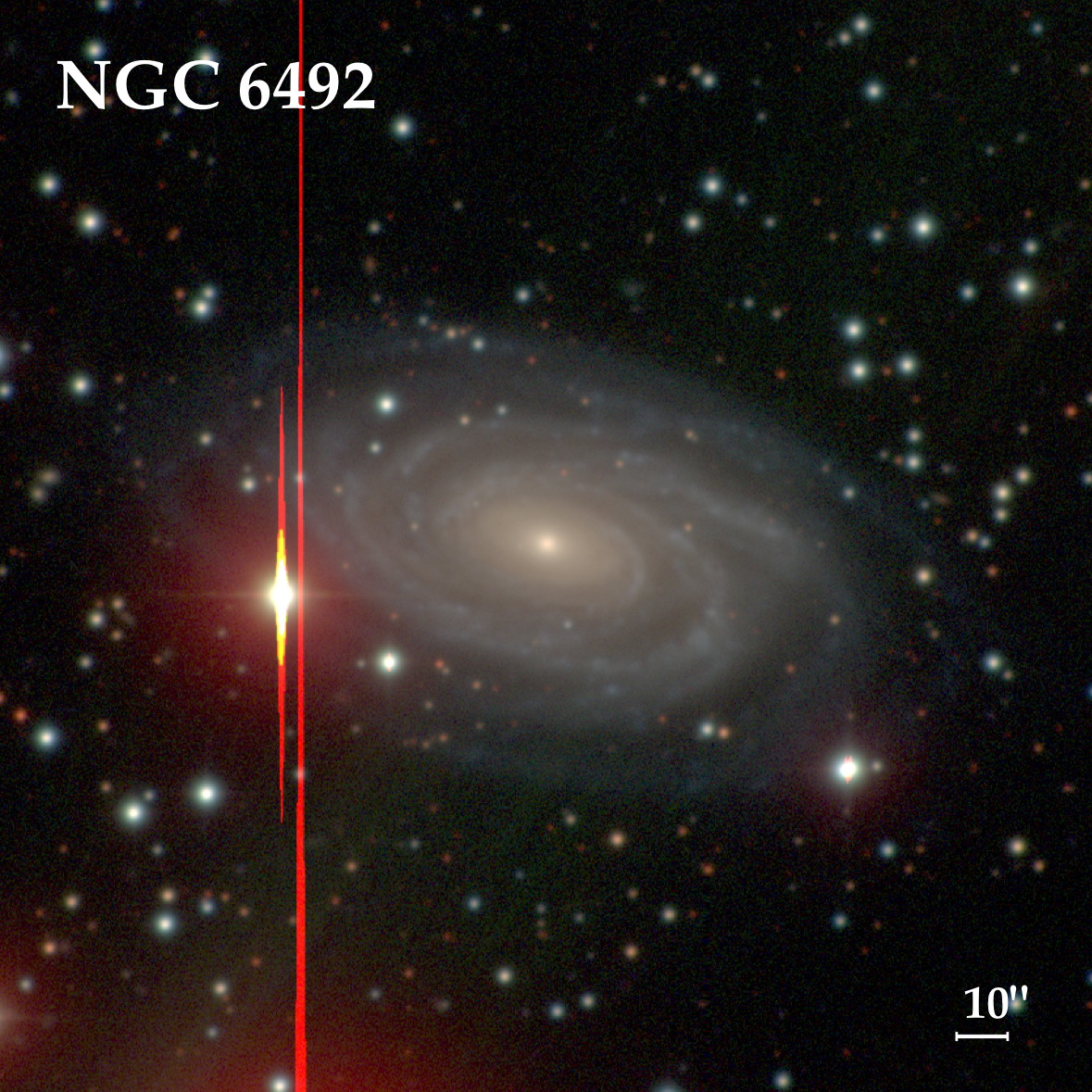
NGC 6492 is a spiral galaxy in the constellation of Pavo. Its velocity with respect to the cosmic microwave background is 4351 ± 8 km/s, which corresponds to a Hubble distance of 209.3 ± 14.6 Mly (64.17 ± 4.49 Mpc). In addition, five non redshift measurements give a distance of 183.10 ± 12.28 Mly (56.140 ± 3.766 Mpc). The galaxy was discovered by British astronomer John Herschel on 22 July 1835.
The SIMBAD database lists NGC 6492 as a Seyfert II Galaxy, i.e. it has a quasar-like nucleus with very high surface brightnesses whose spectra reveal strong, high-ionisation emission lines, but unlike quasars, the host galaxy is clearly detectable.
Supernovae
Two supernovae have been observed in NGC 6492:
- South African amateur astronomer Berto Monard discovered SN 2004fv (type Ia, mag. 14.8) on 4 November 2004.
- The GOTO telescope array discovered SN 2024sky (type II, mag. 16.65) on 19 August 2024.
See also
- List of NGC objects (6001–7000)
References
External links
- NGC 6492 on WikiSky: DSS2, SDSS, GALEX, IRAS, Hydrogen α, X-Ray, Astrophoto, Sky Map, Articles and images